Table of Contents
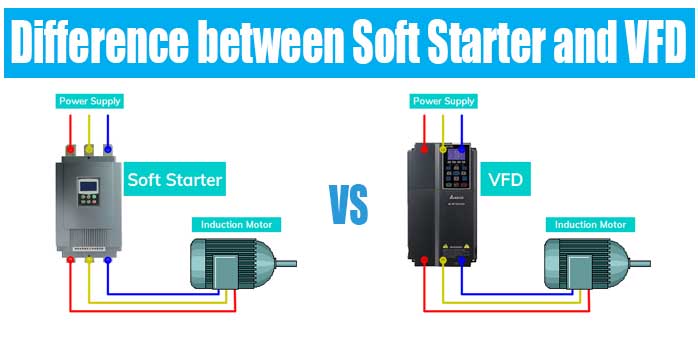
Difference between Soft Starter and VFD
In this article, we will be discussing the difference between Soft Starter and VFD (Variable Frequency Drive). But before that I recommend you to quickly read our previous articles about VFD and Soft Starter by clicking the below links:
What is Variable Frequency Drive?
Industrial motor control often requires a large amount of energy to accelerate the motor quickly at full speed.
Soft Starter and VFD both are widely used in the industry. Both are working similarly in starting and stopping of an industrial motor but have different characteristics.
Why do we use Soft Starter and VFD?
When we start an industrial motor by DOL or other conventional starters, it would drain heavy inrush current (Generally 4 to 6 times of its full load current). Frequent start and stop can decrease the life of the motors.
Soft Starter and VFD can be both used to reduce inrush currents and limit torque-thus protecting the valuable equipment. It also reduces the heat generated by frequent start/stop and thus extending the life of the motor.
Choosing between a soft starter and a variable frequency drive depends on the various parameter such as type of application, system requirements and initial cost.
Soft Starters
A soft starter is a solid-state device that is used to protect an industrial motor from the damage caused by sudden influxes of power. Soft starter limits the large inrush current during motor power-up by reducing the voltage. Therefore, it is also known as reduced voltage soft starters(RVSS).
Applications
Soft starters are generally used in applications where,
- Speed and torque control required only during start/stop.
- Reducing huge startup inrush current associated with a large motor.
- Mechanical equipment requires a gentle start to relieve torque spikes and tension associated with normal startup.
- Pumps, Blowers are used to eliminating pressure surges caused in a piping system.
How does a soft starter work?
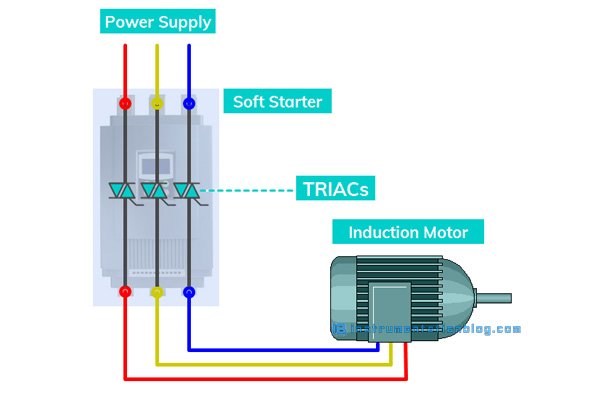
A soft starter uses six thyristors or SCRs in reverse-parallel configuration to start the motor smoothly. A thyristor is made up of anode, cathode, and gate.
When there is a pulse at the gate terminal it allows the current to flow from anode to cathode and this is the ON state of the thyristor. And when there is no pulse at the gate terminal, it restricts the current to flow. This is the OFF state of the thyristor.
The pulses at the gate terminal are controlled based on the ramp-up time and thus controlled the applied voltage to an electric motor. The motor attached with the soft starter will start up smoothly with a nice and smooth current until it reaches at a maximum speed.
Benefits of choosing a soft starter
Soft starters are often the economical choice for applications that require speed and torque control only during motor startup.
Even when the space is concern then soft starter is the best choice, because it requires less space as compared to variable frequency drive.
Variable Frequency Drives
A variable frequency drive is a type of device that controls the speed of an electrical motor by varying the frequency and voltage of its power supply. The VFD also has ramp-up and ramp-down facilities to start and stop the electrical motor smoothly throughout the run cycle. VFDs are also referred to as adjustable frequency drives (AFDs).
Applications
VFDs are used in applications where:
- Complete speed control is required.
- Energy saving is the main goal.
- Custom control is required.
How does a variable frequency drive work?
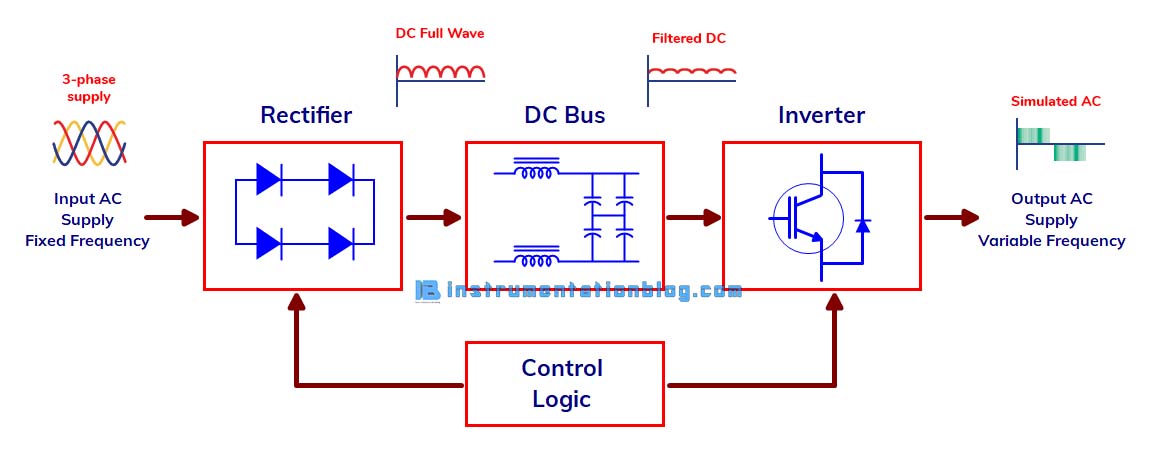
The VFD has mainly four sections:
1. AC to DC Converter (Rectifier): It converts AC supply from the main power supply into DC supply.
2. DC Link: The main function of the DC link is to store, smooth, and deliver the DC voltage. This section of the VFD contains capacitors and inductors.
3. DC to AC Converter (Inverter): The DC voltage is converted back into AC voltage to feed to the motor. In this section of VFD, a DC voltage from the DC link is converted into AC voltage using transistors, IGBT, or thyristors.
4. Control Circuit: Each drive consists of control circuitry, which is used to parameterize the drive. It consists of a microprocessor-based unit that performs various functions such as controlling the speed of the motor, monitoring the alarms and faults of the ac drive, interfacing the ac drive with different devices using a communication protocol, etc.
Benefits of choosing VFDs
- Energy Savings
- Reduces peak energy demand
- Reduces power when not required
- Controlled starting, stopping, and acceleration
- Dynamic torque control
- Provides smooth motion for applications such as elevators, escalators
- Maintain speed of equipment such as mixers, grinders, crushers, etc.
- Advanced overload protection
- Communication with PLC, HMI, DCS, etc.
- Relay Outputs
Difference between Soft starter and VFD
| Soft Starter | Variable Frequency Drive |
| A soft starter is used only during start/stop smoothly an induction motor. | VFD is used to start, stop the motor smoothly and even control the speed throughout the operation. |
| Soft starters are bypassed as the electrical motor reaches its full speed. | VFDs are used to control the speed of the motor throughout the operation. |
| Soft starters do not inject harmonic noise. | VFD induces harmonic noise. An extra filter is required to reduce the noise. |
| Energy saving is less. | VFD can save more energy. |
Choosing between Soft Starter and VFD
Choosing a soft starter or VFD that totally depends on your applications.
⇒ Soft starters are smaller in size and less expensive as compared to VFDs.
⇒ Initial cost of the VFDs are more expensive as compared with the soft starter, but VFDs also provide energy saving up to 50% thereby producing more cost-saving over the life of the equipment.
⇒ VFDs can control the speed of the motor throughout the operation, not just during start-up as soft starter.
⇒ If the application does not require constant acceleration control and requires current limiting only at start-up, then only a soft starter is the better solution from a cost standpoint.
Next Must-Read Articles
- What is Soft Starter and How does it work?
- What is VFD (Variable Frequency Drive)?
- How does a Pulse Width Modulation work in VFD?
- What are the differences between a Sensor and a Transducer?
- What is Smart Transmitter?
- What is Temperature Scanner and How does it work?
- What is a servo motor and how does it work?
- What is Pyrometer?
You can read more articles about Electrical and you can also find books that boost your knowledge in the field of Instrumentation ⇒
Thanks for reading!