Hi! Programmers! How are you? I hope you all are good and doing well in your life.
Everybody we communicate via the help of languages, without this language it’s very hard to convey our messages with each other. Exactly in the same way different automation devices are communicating with each other via standard communication protocols.
Today, in this article, we are going to study different PLC communication protocols. So further not waste more time and let’s start the topic.
Table of Contents
What is PLC Communication Protocol?
To know about PLC Communication protocols, first, we have to know what is communication protocol?
I like the definition of communication protocol as per startupandroid.com,
The communication protocol is a set of rules that sends and receives data between two or more communicating devices.
The communication protocol act as a way between devices to connect and communicate with each other. Without communication protocol devices are just only connected with each other but they can’t be communicated with each other.
So we can say that the communication protocols which PLC is using to communicate with different field devices, programming devices, other PLCs as well as controllers, HMIs, SCADAs, etc. are called PLC communication protocols.
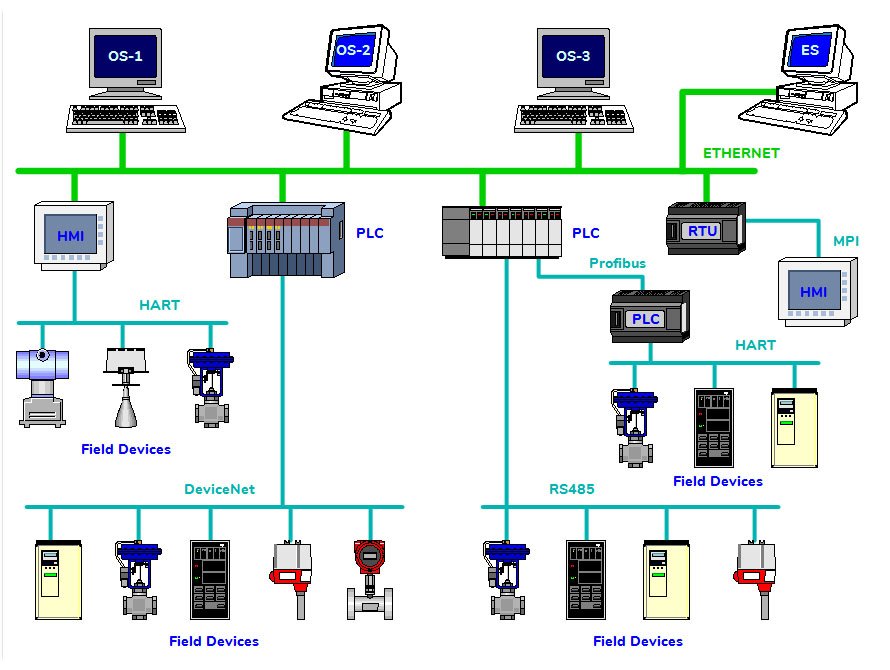
List of Communication Protocols
- AS-i – Actuator-sensor interface
- BSAP – Bristol Standard Asynchronous Protocol
- CC-Link Industrial Networks
- CIP (Common Industrial Protocol)
- ControlNet
- DeviceNet
- DF-1
- DNP3
- DirectNet
- EtherCAT
- Ethernet Global Data (EGD)
- EtherNet/IP
- Ethernet Powerlink
- FINS
- FOUNDATION Fieldbus – H1 & HSE
- HART Protocol
- HostLink Protocol
- Interbus
- MECHATROLINK
- MelsecNet, and MelsecNet II, /B, and /H
- Modbus PEMEX
- Modbus Plus
- Modbus RTU or ASCII or TCP
- OSGP – The Open Smart Grid Protocol
- OpenADR – Open Automated Demand Response
- Optomux
- PieP – An Open Fieldbus Protocol
- Profibus
- PROFINET
- RAPIEnet
- Honeywell SDS
- SERCOS III
- SERCOS interface
- GE SRTP
- Sinec H1
- SynqNet
- TTEthernet
- MPI – Multi-Point Interface
This is the list of communication protocols used by different brands of PLCs as well as other control devices. You can buy the hardware required to communicate different automation devices from this link.
Important Parts of Communication Protocols
There are some important parts on which you can decide which communication protocol is best for your application, like
- Baud Rate
- Network Length
- Number of nodes
Baud Rate ⇒
Baud Rate is the rate of transmission at which information is transferred in the communication channel. Baud rate is generally defined as the communication speed. The unit of baud rate is bps(bits per second).
Network Length ⇒
Network length is the total length of the network.
Number of nodes ⇒
Nodes represent the total number of devices connected to the network.
The below table represents the speed, length, and a maximum number of devices you can connect with this protocol.
| Protocol | Baud Rate | Network Length | Number of nodes |
| Ethernet | 100 Mb/s | 100 m | 255 |
| Profibus | 9.6 Kb/s – 12 Mb/s | 1.2 km – 100 m | 127 |
| RS-232 | 19.2 Kb/s | 10 m | 1 |
| RS-485 | 10 Mb/s | 1.2 Km | 32 |
| MPI | 19.2 – 38.4 Kb/s | 50 m | 32 |
| PPI | 187.5 Kb/s | 500 m | 1 |
| DH | 230.4 Kb/s | 3.048 m | 64 |
| ControlNet | 5 Mb/s | 1000 m | 99 |
| DeviceNet | 500 Kb/s | 100 m | 64 |
Which communication protocol you should use?
- This primarily depends on the number of nodes or devices you want to connect and how much is your network length? The most commonly used communication protocol is Ethernet.
Must-read Articles ⇒
⇒ PLC Timer and PLC Counter
⇒ What is OPC? How does OPC work?
I hope you like this article about PLC communication protocols. If you have any questions then please comment down below. Each comment matters for us and gives us the motivation to share more knowledge with you all.
You can read more articles about Electrical and you can also find books that boost your knowledge in the field of Instrumentation ⇒
Thanks for reading!
