Table of Contents
What is Instrument Transformers?
Generally in a power transmission system, the magnitude of the voltage and current is very high. So, we need an accurate device that measures this high magnitude. An instrument transformer is a device that is used to measure the voltage and current in an AC system. It is used to measure electrical quantities such as voltage, current, power, power factor, frequency, energy, etc. An instrument transformer is used with the protective relays for the protection of the power system.
The transformer is a device that is used to step up or down the voltage and current. The basic function of an instrument transformer is to step down the AC system voltage and current. Generally, the measuring value for the voltage is 110V, and the current is 1A or 5A.
Instrument transformer plays an important role in a modern power system because it is used to measure as well as protect the power system.
Types of Instrument Transformer
There are mainly two types of instrument transformer generally used in power system,
- Current Transformer (CT)
- Potential Transformer (PT)
Current Transformer (CT)
A current transformer is a device that is used to convert a higher value of current into a proportionate value. It steps down the current to a value that we can measure the heavy flow of current through the transmission lines and is safely monitored by the ammeter.
The connection diagram of the current transformer is as shown in the figure.
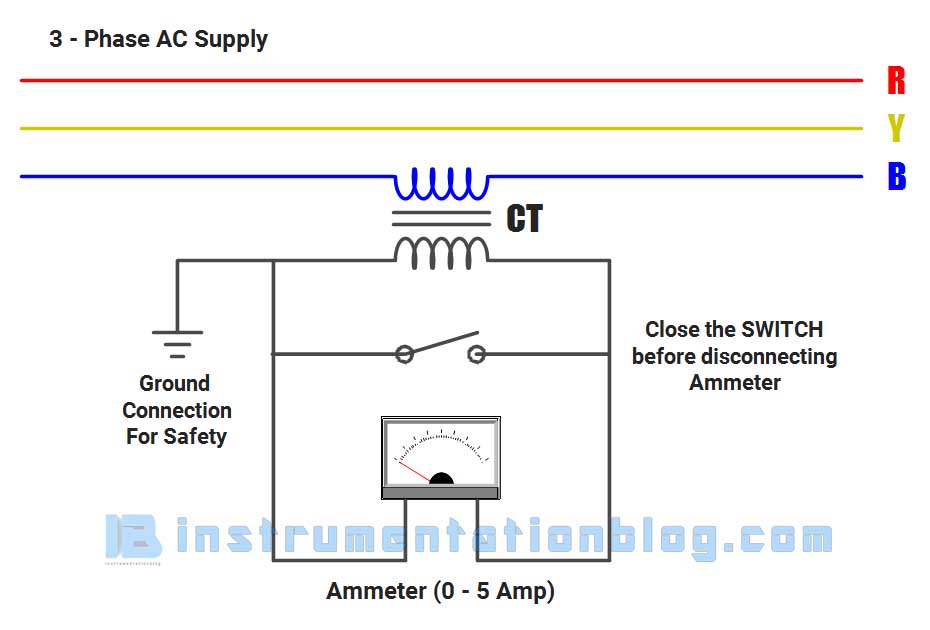
The primary windings of the current transformer are connected directly in series with the power circuit. The secondary windings of the current transformer are connected to an ammeter. One terminal of the secondary windings is earthed to avoid large voltage on secondary with respect to the earth.
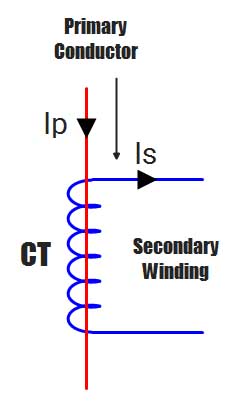
The current ratings for the secondary winding are usually 1A or 5A and for the primary winding vary from 10A to 3000A. The symbolic representation of the current transformer is as shown below.
Potential Transformer (PT)
The potential transformer is a device that is used to step down the higher voltage value to a lower value that can be easily monitored and measured. It is also known as a voltage transformer or instrument transformer.
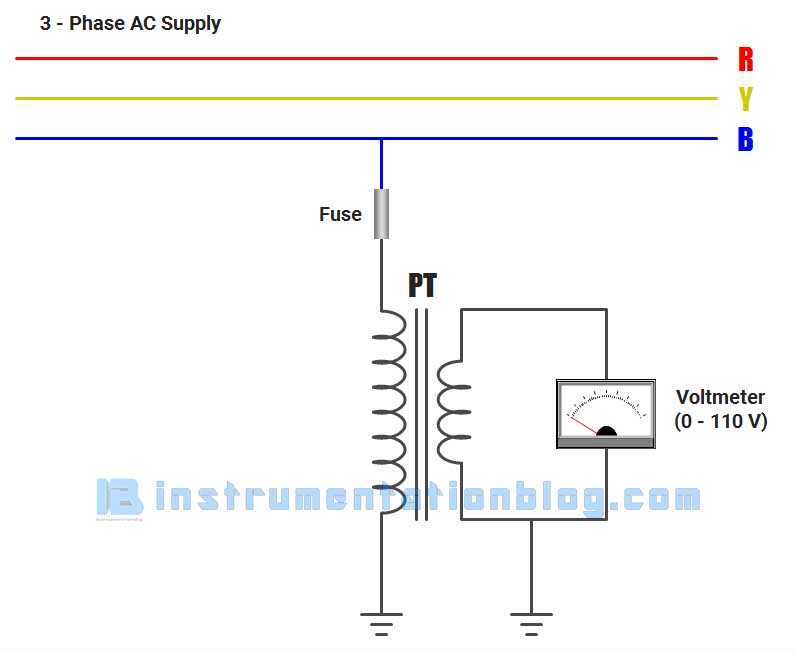
Like a conventional transformer, we can find primary and secondary windings in a potential transformer. The primary windings have large numbers of turns as compared to the secondary winding. One terminal of this winding is connected to the earth to maintain the voltage with respect to the earth to protect the operator from a huge voltage.
The power system voltage is directly applied to the primary windings of the potential transformer and proportionate secondary voltage appears across the secondary terminals of the PT. The voltmeter has a large resistance, hence the secondary of the PT works in an open circuit condition. The value of the secondary voltage generally is 110V.
Difference between CT and PT
There are few differences between CT and PT, such as:
| Current Transformer (CT) | Potential Transformer (PT) |
| Connected in series with power circuit. | Connected in parallel with power circuit. |
| The secondary is connected to Ammeter. | The secondary is connected to Voltmeter. |
| The secondary works almost in short-circuit condition. | The secondary works almost in open-circuit condition. |
| One terminal of the secondary is earthed to avoid the insulation break down. | One terminal of the secondary can be earthed for safety. |
| The primary current depends on the power circuit current. | The primary current depends on the secondary burden. |
| The transformer ratio is high. | The transformer ratio is low. |
| The impedance of the transformer is low. | The impedance of the transformer is high. |
| The secondary is never to be open-circuited. | The secondary can be used in open circuit conditions. |
Advantages of Instrument Transformer
⇒ It provides electrical isolation among the measuring instruments and high power circuits.
⇒ By using an instrument transformer, several protecting devices can be operated like relays.
⇒ Various measuring instruments can be connected using this transformer.
Frequently Asked Questions,
1) What are CT and PT in the instrument transformers?
Current Transformer (CT) and Potential Transformer (PT) are measuring devices used in high voltage power circuit systems.
2) What are the applications of instrument transformers?
Instrument transformers are used mainly in measurement and protective equipment. They are also used to operate protective relays.
3) What are the advantages of instrument transformers?
Instrument transformers provide electrical isolation between the measuring circuits and high voltage power circuits.
4) What are the three main parts of a transformer?
- An iron core serves as a magnetic conductor.
- A primary winding.
- A secondary winding.
Next Must-Read Articles
- The most used 3 Basic Motor Starter with its PLC Program!
- What is Temperature Scanner? How does it work?
- What is the Servo Motor? How does it work?
- How star-delta starter works?
- What is Soft Starter? How it works?
- Circuit Breaker Fundamentals.
- Relay Working and its importance in an electrical field.
You can read more articles about Electrical and you can also find books that boost your knowledge in the field of Instrumentation ⇒
Thanks for reading!