Table of Contents
What is Pyrometer? Types, Advantages, Applications, etc.
Temperature measurement is a critical parameter for any industry. A high degree of precision is required while measuring temperature.
A pyrometer is a device that is used to measure a high degree of temperature without being in contact with any device. The pyrometer uses heat/radiation from the object’s body to measure the temperature.
The pyrometer offers the following features, such as
⇒ Non-contact measurement of temperature
⇒ Easy measurement in places that are difficult to access
⇒ Very precise and Reliable temperature measurement technology
Pyrometer Definition
A pyrometer is a device that is used to measure relatively high temperatures. Pyrometer works on the principle of radiation or heat from the object’s body to measure the temperature, that’s why it has the advantage to measure the temperature without being touch the material being measured.
A modern definition would be like, a pyrometer is a non-contacting device to measure the thermal radiation from the object to measure the surface temperature.
Types of Pyrometer
The pyrometer can be classified into mainly two types based on it’s working principle,
⇒ Optical Pyrometer
⇒ Infrared/Radiation Pyrometer
Optical Pyrometer
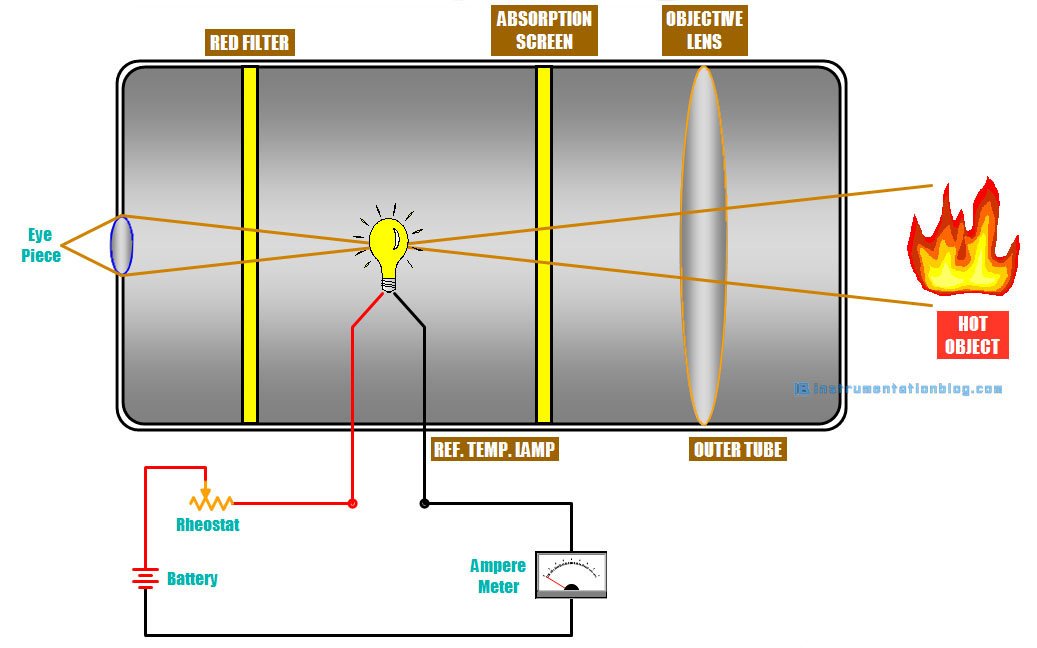
From the above image, we can see the parts of the optical pyrometer.
⇒ An eyepiece or observer is on the left side and an optical lens on the right side.
⇒ A lamp that generates reference temperature using a power source and rheostat.
⇒ An ampere meter to measure the current to calculate the temperature.
⇒ An absorption screen is installed between the lens and a reference lamp.
⇒ A red filter between the reference lamp and eyepiece or observer.
Any object whose temperature is absolute zero emits or generates radiation. This emission depends on the temperature of the object.
An optical pyrometer uses this radiation to measure the temperature of the object. The brightness of the measured object is compared with the brightness of the lamp at a reference temperature.
The reference temperature is produced by the lamp whose brightness can be adjusted using rheostat as shown in the above figure.
How does it work?
Any object whose temperature is absolute zero emits or generates radiation. This emission depends on the temperature of the object.
The radiation from the source is captured by the optical lens. The lens helps in focusing the thermal radiation on the lamp.
The observer starts observing the brightness of the lamp filament. The filament of the reference lamp is superimposed on the temperature of the source. The observer starts changing the rheostat value.
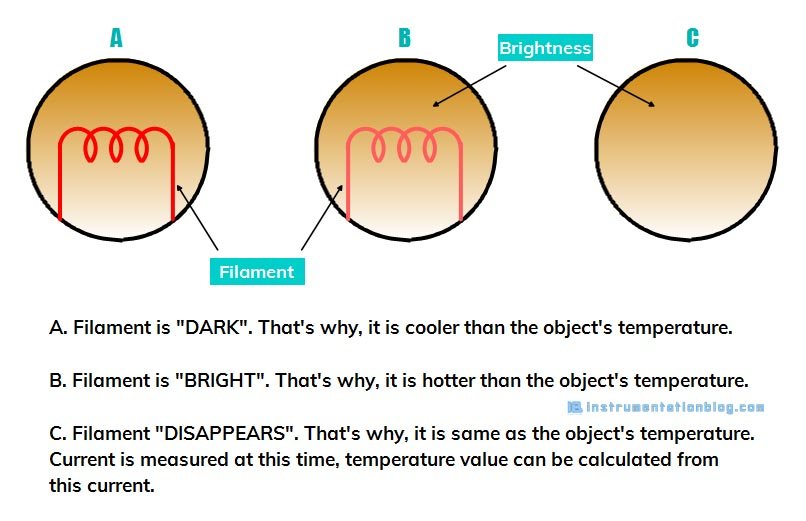
There may be three possibilities, such as
A. When the filament is “DARK“. Then the source object is hotter than the reference temperature or we can say that the filament temperature is cooler than the source temperature.
B. When the filament is “BRIGHT“. Then the source object is cooler than the reference temperature or we can say that the filament temperature is hotter than the source temperature.
C. When the filament “DISAPPEARS“. So we can say that the temperature of the source object and reference temperature is the same.
At this time current can be measured to calculate the temperature.
Advantages
- Assembly is simple and portable.
- Provides a very high accuracy with the tolerance of ±5 ºC.
- No need to be in direct contact with the object whose temperature is being measured.
- Useful for the temperature measurement of the moving objects.
- It can be used easily at a place where a physical approach is possible to measure the temperature.
Disadvantage
- Measurement is completely based on the light intensity, it can be useful only to measure relatively high temperature.
Infrared/Radiation Pyrometer
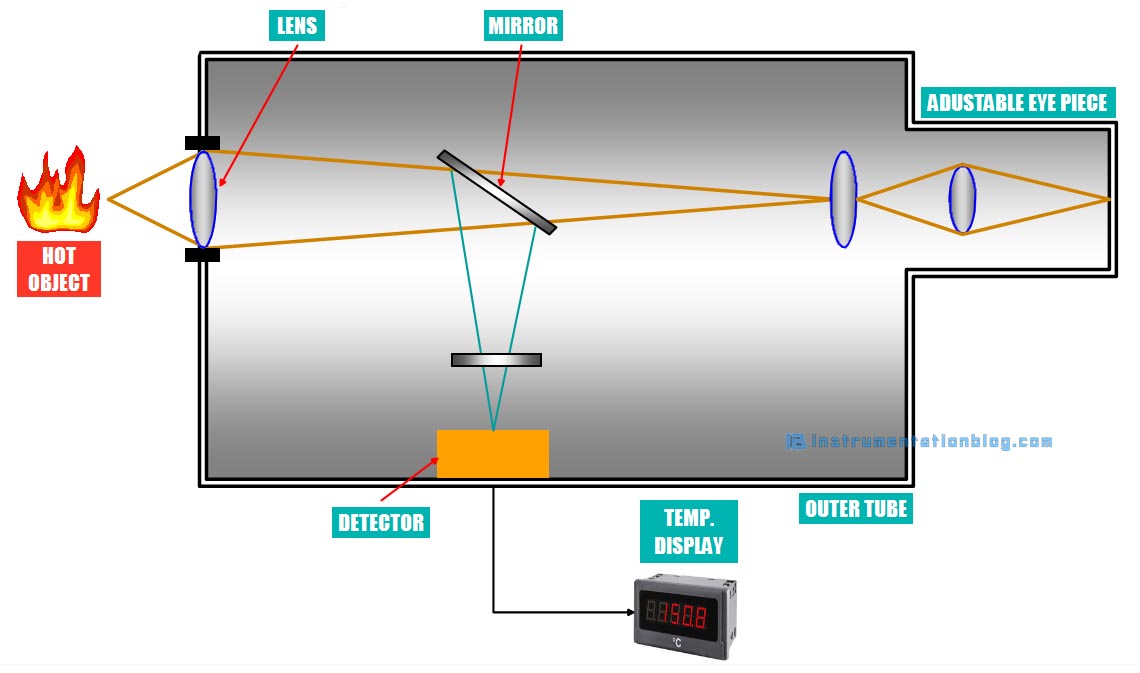
As shown in the figure, the radiation pyrometer has an optical system such as it has an optical lens, mirror, and adjustable eyepiece. The heat energy is transferred through the optical lens to the mirror. The mirror focuses this energy on the detector.
The detector may be either thermopile or photomultiplier tubes. The photomultiplier tubes are much faster than the thermopile. Thus temperature measurement is much faster when used photomultiplier tubes. The detector converts the collected heat energy into an electrical current signal and drives it to the control unit or temperature display.
Advantages
- It has a high performance and moderate cost.
- It has a fast speed response.
- It has good stability.
- No need to be in physical contact with the object being measured.
Disadvantage
- The design of the radiation pyrometer is complex.
- The emissivity of the target material may affect the measurement.
Application of Pyrometer
These are some examples where pyrometer is used for temperature measurement,
⇒ Blast Furnace temperature measurement.
⇒ Smelter Industry
⇒ Metallurgical Furnace operation where the temperature is the critical parameter.
⇒ Steam Boiler
⇒ Gas Turbine Engines
⇒ Hot Air Balloon.
If you like this blog, please share it with your friends and colleagues and give your feedback in the comment section below.
You can read more articles about Instrumentations and find books that boost your knowledge in the field of instrumentation ⇒
Thanks for reading!
This is a very good explanation.
I love the explanation. It is have the major points that needs for explanation.
Very good explanation dear